French Guiana topographic map
Interactive map
Click on the map to display elevation.
French Guiana
French Guiana has an equatorial climate predominant. Located within six degrees of the Equator and rising only to modest elevations, French Guiana is hot and oppressively humid all year round. During most of the year, rainfall across the country is heavy due to the presence of the Intertropical Convergence Zone and its powerful thunderstorm cells. In most parts of French Guiana, rainfall is always heavy especially from December to July – typically over 330 millimetres or 13 inches can be expected each month during this period throughout the department. Between August and November, the eastern half experiences a warm dry season with rainfall below 100 millimetres or 3.94 inches and average high temperatures above 30 °C (86 °F) occurring in September and October, causing eastern French Guiana to be classified as a tropical monsoon climate (Köppen Am); Saint-Laurent-du-Maroni in the west has a tropical rainforest climate (Af).
About this map
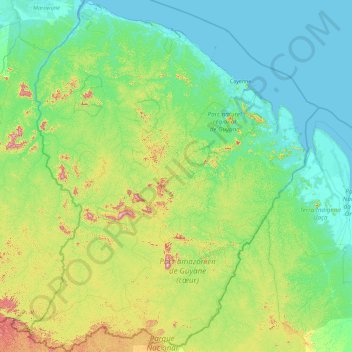
Name: French Guiana topographic map, elevation, terrain.
Location: French Guiana, France (2.11094 -54.60269 5.77695 -51.63461)
Average elevation: 338 ft
Minimum elevation: -7 ft
Maximum elevation: 2,595 ft
Other topographic maps
Click on a map to view its topography, its elevation and its terrain.
Paris
Paris in its early history had only the rivers Seine and Bièvre for water. From 1809, the Canal de l'Ourcq provided Paris with water from less-polluted rivers to the north-east of the capital. From 1857, the civil engineer Eugène Belgrand, under Napoleon III, oversaw the construction of a series of new…
Average elevation: 246 ft
Château du Planchat
France > Nouvelle-Aquitaine > Dordogne > Montignac-Lascaux
Average elevation: 518 ft
La Gravette
France > Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur > Alpes-de-Haute-Provence > Barcelonnette
Average elevation: 4,206 ft
Jardins de la Rainville
France > Centre-Val de Loire > Eure-et-Loir > Châteaudun
Average elevation: 430 ft
Plage du Canon
France > Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur > Var > Saint-Mandrier-sur-Mer
Average elevation: 59 ft
Sauveterre
France > Occitania > Lozère > Gorges du Tarn Causses > Sainte-Enimie
Average elevation: 3,271 ft
Mollard Durand
France > Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes > Savoy > Saint-Martin-de-la-Porte
Average elevation: 3,445 ft
Pièce de Givry
France > Centre-Val de Loire > Indre-et-Loire > Athée-sur-Cher
Average elevation: 302 ft
Etang des Lames
France > Bourgogne – Franche-Comté > Yonne > Island > La Courcelle
Average elevation: 922 ft
Col de Nice
France > Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur > Maritime Alps > L'Escarène
Average elevation: 1,463 ft
Serre Chevalier
France > Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur > Hautes-Alpes > Puy-Saint-André
The maximum elevation for skiing is at Telesiege Yret at 2,800 m (9,190 ft) above sea level, and the minimum is 1,200 m (3,940 ft), a total vertical drop of 1,600 m (5,250 ft). One of the outstanding features of Serre Chevalier is the wooded nature of the slopes. The timber line is at 2,150 m (7,050 ft),…
Average elevation: 7,402 ft
La Vieille-Ville
France > Pays de la Loire > Loire-Atlantique > La Chapelle-Glain
Average elevation: 236 ft
Cime de la Bonette
France > Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur > Maritime Alps > Saint-Dalmas-le-Selvage
Average elevation: 8,241 ft
La Grande Ragotière
France > Pays de la Loire > Loire-Atlantique > La Regrippière
Average elevation: 262 ft
Mont Agel
France > Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur > Maritime Alps > Peille
Mont Agel is a mountain in the Maritime Alps on the border between France and Monaco. The summit of this mount, at 1,148 metres (3,766 ft) above sea level, is on the French side, but the highest point of Monaco, lying on a pathway named Chemin des Révoires, is on its slopes, at an altitude of 161 metres (528…
Average elevation: 2,592 ft
Étang des Vosges
France > Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes > Ain > Saint-Germain-sur-Renon > La Maison Neuve
Average elevation: 899 ft
Bayonne
France > New Aquitaine > Pyrénées-Atlantiques > Bayonne > Bayonne
In the late Quaternary, the current topographic physiognomy was formed—i.e. a set of hills overlooking a swampy lowland. The promontory of Bassussarry–Marracq ultimately extended to the Labourdin foothills. The Grand Bayonne hill is an example. Similarly, on the right bank of the Nive, the heights of…
Average elevation: 75 ft
Danton
France > Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes > Ardèche > Saint-Sauveur-de-Montagut
Average elevation: 1,588 ft
Le Moulin Géant
France > Pays de la Loire > Maine-et-Loire > Rochefort-sur-Loire
Average elevation: 151 ft
L'Égronnière
France > Pays de la Loire > Vendée > Montaigu-Vendée > Saint-Hilaire-de-Loulay
Average elevation: 138 ft
Mont Auxois
France > Bourgogne-Franche-Comté > Côte-d'Or > Alise-Sainte-Reine
Average elevation: 1,007 ft
Bois Grillots
France > Ile-de-France > Seine-et-Marne > Moret-Loing-et-Orvanne
Average elevation: 259 ft
