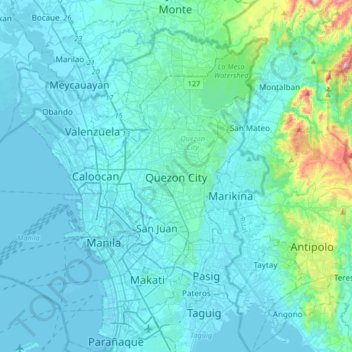
Quezon City topographic map
Interactive map
Click on the map to display elevation.
About this map
Founded as a pueblo by Saint Pedro Bautista in 1590, San Francisco del Monte may be considered Quezon City's oldest district. The original land area of the old town of San Francisco del Monte was approximately2.5 square kilometres (1.0 sq mi) and covered parts of what is currently known as Project 7 and 8 and Timog Avenue. It was later absorbed by Quezon City. It featured a hilly topography with lush vegetation and mineral springs, in the midst of which the old Santuario de San Pedro Bautista was built as a retreat and monastery for Franciscan friars.
Other topographic maps
Click on a map to view its topography, its elevation and its terrain.
Lipa
Philippines > Batangas > Lipa > Lipa
Lipa, Batangas, Calabarzon, 4217, Philippines
Average elevation: 535 ft
Cavite City
Philippines > Cavite > Cavite City
Cavite City, Cavite, Calabarzon, 4100, Philippines
Average elevation: 43 ft
San Mateo
San Mateo, Rizal, Calabarzon, 1631, Philippines
Average elevation: 223 ft
Calinan District
Calinan District, Davao City, Davao Region, 8018, Philippines
Average elevation: 784 ft
Nabuslot
Philippines > Oriental Mindoro > Pinamalayan
Nabuslot, Pinamalayan, Oriental Mindoro, Mimaropa, 5208, Philippines
Average elevation: 49 ft
Lucanin
Philippines > Bataan > Mariveles
Lucanin, Mariveles, Bataan, Central Luzon, Philippines
Average elevation: 75 ft
Kinawe
Philippines > Bukidnon > Libona
Kinawe, Libona, Bukidnon, Northern Mindanao, 8706, Philippines
Average elevation: 994 ft
Cebu City
Philippines > Cebu > Cebu City
Cebu City, Cebu, Central Visayas, 6000, Philippines
Average elevation: 459 ft
Cogon
Philippines > Cebu > Cordova
Cogon, Cordova, Cebu, Central Visayas, 6017, Philippines
Average elevation: 7 ft
La Paz
La Paz, 2nd District, Leyte, Eastern Visayas, 6508, Philippines
Average elevation: 141 ft
Aramal
Philippines > Pangasinan > San Fabian
Aramal, San Fabian, Pangasinan, Ilocos Region, 2433, Philippines
Average elevation: 49 ft
Canumay West
Canumay West, 1st District, Valenzuela, Northern Manila District, Metro Manila, 1447, Philippines
Average elevation: 49 ft
Sto. Niño
Philippines > Occidental Mindoro > Sablayan
Sto. Niño, Sablayan, Occidental Mindoro, Mimaropa, 5104, Philippines
Average elevation: 43 ft
Burabud
Philippines > Leyte > Jaro > District Ⅱ
Burabud, District Ⅱ, Jaro, 2nd District, Leyte, Eastern Visayas, 6527, Philippines
Average elevation: 331 ft
Baguio
Baguio, Cordillera Administrative Region, 2600, Philippines
Average elevation: 2,890 ft
Miagao
Miagao, Iloilo, Western Visayas, 5023, Philippines
Average elevation: 318 ft
Dit
Philippines > Palawan > Agutaya
Dit, Agutaya, Palawan, Mimaropa, 5320, Philippines
Average elevation: 112 ft
Barangay ng mga Mangingisda
Barangay ng mga Mangingisda, Puerto Princesa, Mimaropa, Philippines
Average elevation: 16 ft
Alabat Island
Alabat Island, Quezon, Calabarzon, Philippines
Average elevation: 36 ft
Navais
Navais, Iloilo City, Western Visayas, 5000, Philippines
Average elevation: 16 ft
Danicop
Philippines > Catanduanes > Virac
Danicop, Virac, Catanduanes, Bicol Region, 4800, Philippines
Average elevation: 279 ft
Kinalumsan River
Kinalumsan River, Cebu City, Central Visayas, 6000, Philippines
Average elevation: 56 ft
Tamboboan
Philippines > Misamis Oriental
Tamboboan, Misamis Oriental, Northern Mindanao, 9004, Philippines
Average elevation: 2,589 ft
Basak
Basak, Catmondaan, Cebu, Central Visayas, 6005, Philippines
Average elevation: 820 ft
Bambang
Bambang, Nueva Vizcaya, Cagayan Valley, 3702, Philippines
Average elevation: 1,234 ft
Hagdan
Philippines > Cebu > Oslob
Hagdan, Oslob, Cebu, Central Visayas, 6025, Philippines
Average elevation: 410 ft
Cabanglasan
Cabanglasan, Bukidnon, Northern Mindanao, 8723, Philippines
Average elevation: 1,985 ft
Basak
Philippines > Bukidnon > Talakag
Basak, Talakag, Bukidnon, Northern Mindanao, Philippines
Average elevation: 1,791 ft
Homonhon Island
Philippines > Eastern Samar > Cagusu-an
Homonhon Island, Cagusu-an, Eastern Samar, Eastern Visayas, Philippines
Average elevation: 89 ft
Mariveles
Philippines > Bataan > Mariveles
Mariveles, Bataan, Central Luzon, 2105, Philippines
Average elevation: 272 ft
Uson Island
Philippines > Palawan > Coron > Bancuan
Uson Island, Bancuan, Coron, Palawan, Mimaropa, Philippines
Average elevation: 46 ft
Coron Island
Philippines > Palawan > Coron
Coron Island, Coron, Palawan, Mimaropa, Philippines
Average elevation: 121 ft
Intramuros
Intramuros, Fifth District, Manila, Capital District, Metro Manila, 1002, Philippines
Average elevation: 23 ft
Changco
Changco, General Santos, Soccsksargen, 9500, Philippines
Average elevation: 151 ft
Boracay
Philippines > Aklan > Malay
Boracay, Malay, Aklan, Western Visayas, 5608, Philippines
Average elevation: 20 ft
San Vicente
San Vicente, Lapu-Lapu, Central Visayas, Philippines
Average elevation: 7 ft
Padada River
Padada River, Davao del Sur, Davao Region, Philippines
Average elevation: 256 ft